Medical Dermatology
Moles
Moles: Description, Diagnosis and Treatment
Description, Diagnosis, and Treatment in the Dallas Area
What is a Mole?
Moles, also referred to by the medical term “nevi,” can be pigmented or skin colored. They typically appear in shades ranging from pale to brown or black. They arise in the pigment-producing cells (melanocytes) of the skin and can be present at birth or later in life. It is important to consult a licensed dermatologist, such as Dr. Ellen Turner, who examines moles at her Dallas-area practice to provide an accurate diagnosis of the common lesion—as well as any lesions patients may be unsure about.
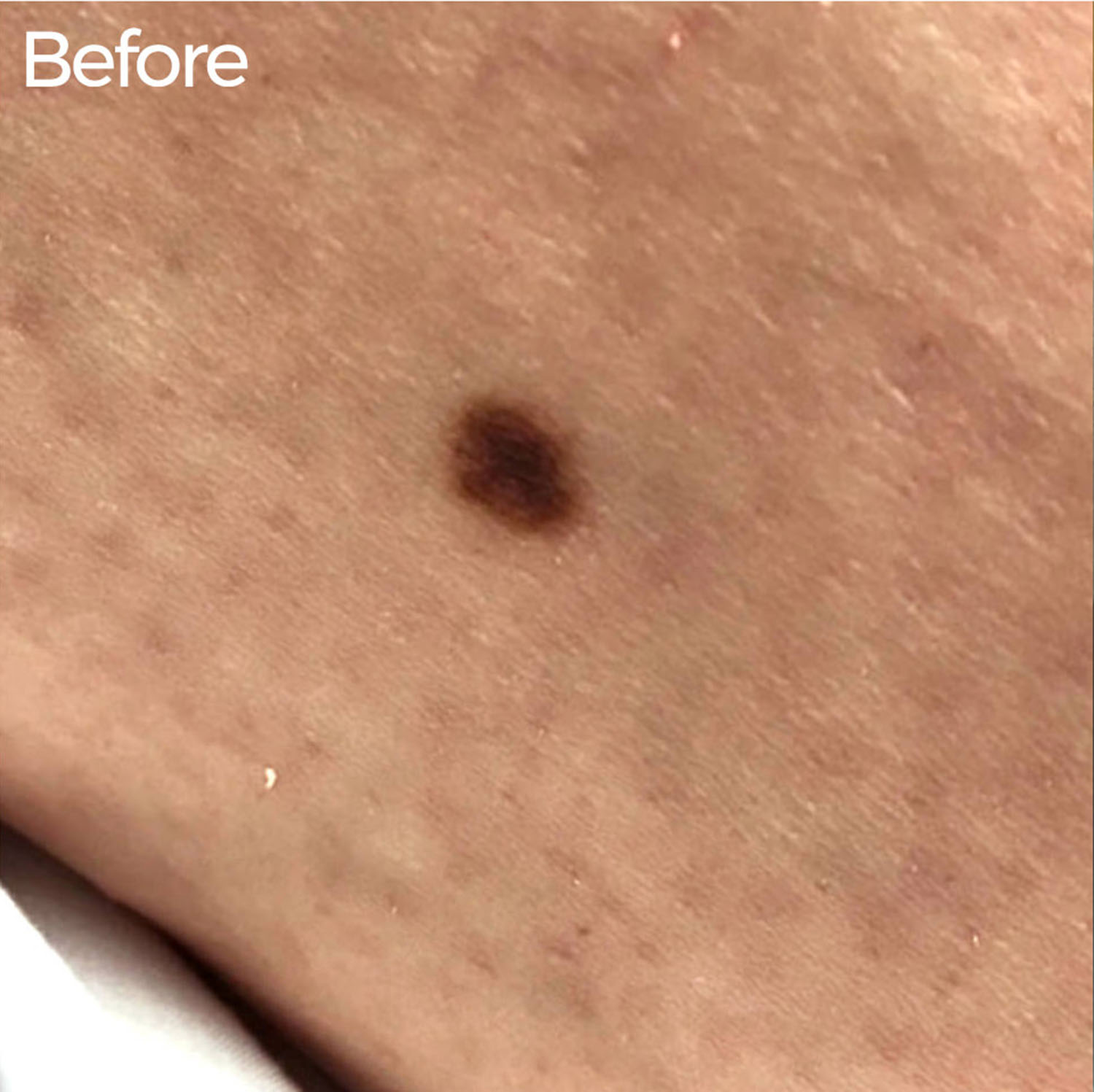
Any new or suspicious spots should be examined by a dermatologist, and concerning lesions should be biopsied. They also may be removed if they become irritated and, in certain instances, for cosmetic reasons. Any mole that grows, changes in shape or color, itches, bleeds, or becomes painful should be evaluated.
Medical Dermatology
Fill out a contact form online or call (214) 373-7546 to schedule an appointment to have an examination for suspicious moles at our Dallas-area locations.
Dermatology Office
Meet Dr. Ellen Turner
Dr. Ellen Turner and her staff at the Dermatology Office strive to work within a space where compassion meets technology to obtain top results for Dallas patients.

Facts About Moles
Moles are basically clusters of pigmented cells—the melanocytes that give your skin its color—that form growths on the skin. It is common for moles to develop throughout childhood. Most of your moles will appear before the age of 25, but some develop later in life as a result of exposure to sunlight. Hormonal shifts may also cause them to change slightly. Moles may be flat or elevated and grow to about the size of a pencil eraser.
They can develop on any part on the body and may disappear with time. It is important to understand that a changing or irregular mole—in other words, one that does not look or act like similar lesions elsewhere on the body—could be an indication of cancer. Patients should check their body all over regularly, especially on areas that are frequently exposed to sunlight, and take note of any changes.
Types of Moles
Common Nevi
Common nevi usually develop sometime between childhood and adolescence. These small spots usually are pink, tan, or brown in color, and they tend to have a uniform round or oval shape with a defined, smooth border. The majority of people have anywhere from 10 to 40 of these nevi in total.
Congenital Nevi
Congenital nevi are the moles that you are born with, rather than developing later in life. These pigmented birthmarks have a slightly higher chance of becoming cancerous compared to common nevi and occur much more rarely.
Dysplastic Nevi
Atypical moles or dysplastic nevi are lesions that have an irregular shape, color, or border. Even if the nevi are noncancerous, they represent an increase in risk of developing melanoma, the deadliest form of skin cancer. They are usually larger than common moles and may be raised.
Treatment for Moles
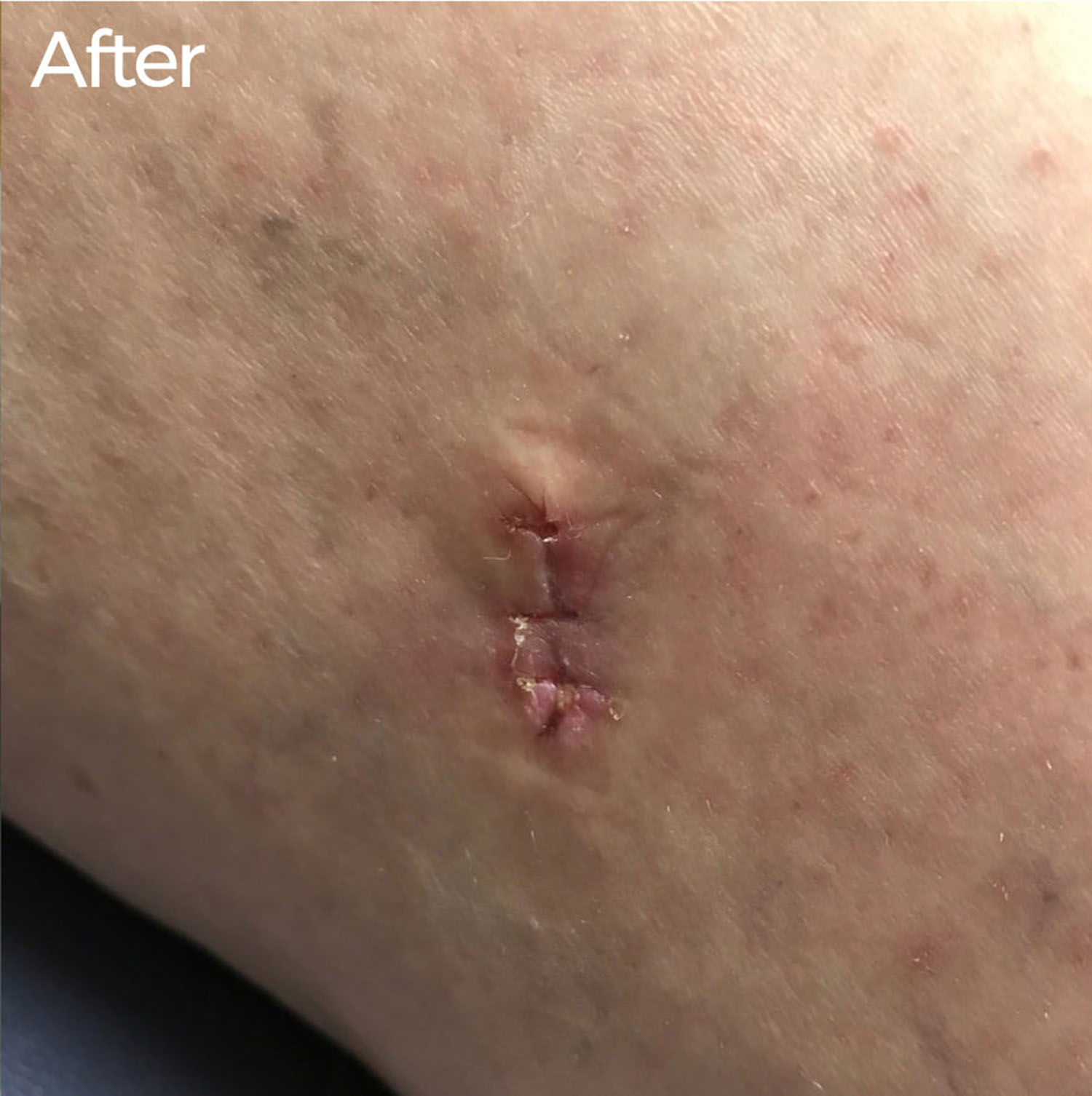
Most moles are harmless and do not require medical treatment, so they can be left alone. However, if Dr. Turner feels treatment is necessary, she can remove a mole during an office visit. Attempting to remove moles at home can be dangerous—and you wouldn’t be able to tell whether it was cancerous, meaning that cancer cells could spread to other areas of the body without you knowing.
A few moles will require a second visit. Whether it’s one or two visits, a licensed dermatologist such as Dr. Turner can safely and easily remove a mole. She will use one of these procedures:
- Surgical excision: Dr. Turner cuts out the entire mole and stitches the skin closed. If she suspects that the mole contains cancer, she will send the specimen to a lab to be examined under a microscope (this is called a biopsy).
- Surgical shave: Dr. Turner uses a surgical blade to remove the mole. No stitches or sutures will be necessary.
- Non-invasive biopsy (DermTech): Dr. Turner has the ability to perform a unique type of test on suspicious moles which are 6mm or larger which can genetically test for markers for melanoma or pre-melanoma without cutting the skin. By utilizing a sticker to remove skin cells from the surface of the mole which are then sent to DermTech laboratories, the cells are tested without creating unnecessary wounds or scarring. Only if there are positive melanoma markers identified will the patient return for actual physical removal of the lesion.
After a mole is removed, the skin will heal. If the mole grows back, it is important to make another appointment to see Dr. Turner, as this may be a sign of melanoma, a type of skin cancer. Because Dr. Turner makes a point to practice outstanding patient care, she is committed to listening to concerns and choosing appropriate courses of action for each patient. People coming to her for a consultation can expect the visit to be pleasant, professional, and educational. To schedule a visit with Dr. Turner to discuss therapeutic options for your moles, book an appointment online or call (214) 373-7546.
How Much Does Mole Treatment Cost?
Costs vary from case to case due to specific treatments and the extent of treatment necessary. Learn more in person or with a phone call.